The word “red crystals” is a general one that could apply to many different kinds of crystals that have a red hue. Crystals can be made of artificial materials with a regular and repeating atomic structure or naturally occurring minerals. A common explanation for crystals’ red hue is the existence of particular minerals, impurities, or flaws.
Red crystals’ vivid, flamboyant colors have always captivated people’s attention. These gemstones have a special place in the fields of metaphysics and crystal healing because of their energy and symbolism. We will explore the intriguing realm of red crystals in this thorough guide, learning about their characteristics, meanings, and the many advantages they may offer you.
Red crystals, ranging from the fervent ruby to the sobering garnet, have a distinct charm that has captivated people for ages. Read on to learn the secrets and wonders of red crystals and yellow crystals, whether you’re an experienced crystal aficionado or just interested in learning more about the world of gemstones.
Table of Contents
Types of Red Crystals
Ruby
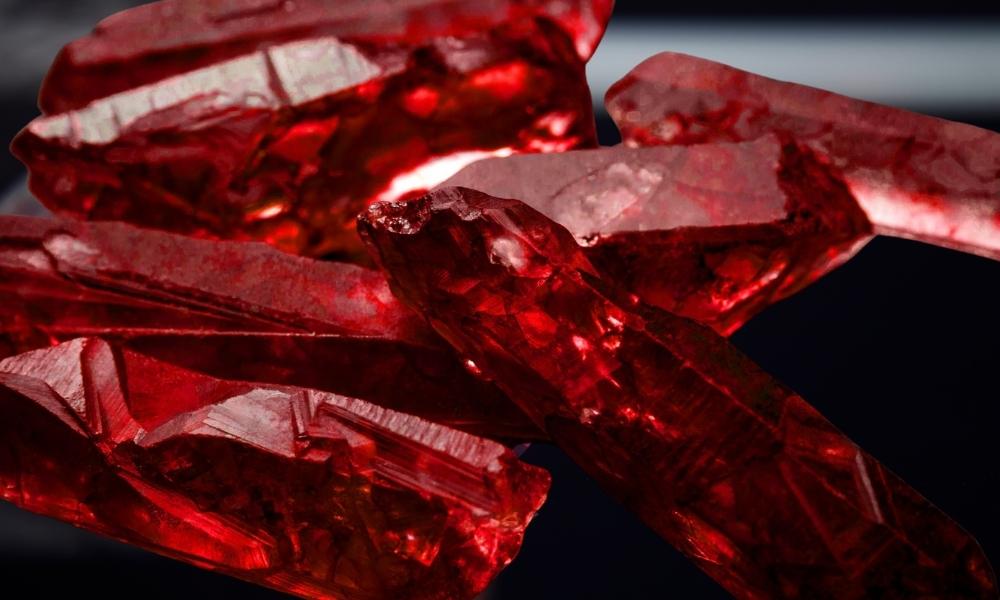

A type of corundum mineral, ruby is a valuable gemstone (aluminum oxide). Ruby is a type of red crystals. It is one of the four valuable gemstones, the others being diamond, emerald, and sapphire. Chromium ions in the crystal lattice structure of rubies give them their vivid red hue. Although the color of red can vary in intensity, the most costly rubies usually have a rich, deep red color.
Here are some key characteristics and information about ruby:
Chemical Composition
Al2O3 is the compound that makes up rubies. Certain aluminum ions are switched out for chromium ions to give the red hue.
Hardness
With a Mohs mineral hardness score of 9, ruby is an exceptionally hard mineral. This makes it a great option for jewelry because it is strong and stain-resistant.
Color
Ruby is best in its purest, brightest red with a touch of blue. This particular tint is commonly known as “pigeon’s blood red.”
Occurrence
While rubies are all over the world, major quantities are in Afghanistan, Madagascar, Thailand, Sri Lanka, and Myanmar (Burma).
Inclusions
Natural rubies frequently have inclusions, which are internal features that determine the origin of the stone. While certain inclusions are acceptable and even thought to be a characteristic of a ruby, others could have an impact on the clarity of the gem.
Treatment
In the ruby industry, heat treatment is a frequent process. It improves the gemstone’s color and clarity. This procedure has been applied to many rubies that are sold.
Symbolism
Ruby has a connection with passion, love, and wealth. It’s also one of the customary birthstones for the month of July.
Red Jasper
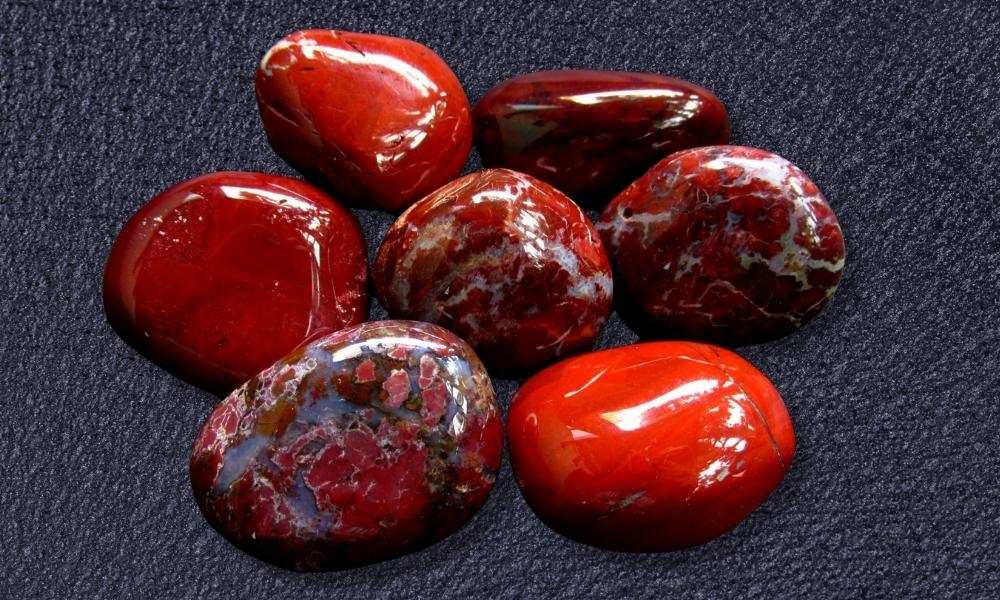

This type of red crystal is one kind of chalcedony, a microcrystalline quartz variant, which is red jasper. Because of the iron oxide inclusions that are present in the stone, it has a distinctively rich red color. Here are some of Red Jasper’s salient characteristics and details.
Color
Red Jasper is mostly red, as the name implies, but it can also show hints of brown, yellow, or even green. The color red can have many patterns and intensities.
Composition
Like other forms of quartz, its primary constituent is silicon dioxide (SiO2). The iron inclusions are what provide the color red.
Hardness
Red Jasper is a somewhat durable stone. Its use is in a variety of jewelry and lapidary applications, with a Mohs hardness of 6.5 to 7.
Occurrence
Red Jasper is all over the world, including the US, Germany, France, Brazil, Russia, India, and Brazil.
Appearance
Red jasper is typically opaque and has a look that is microcrystalline or granular. When polished, it might feel waxy and smooth.
Metaphysical Properties
Some people think red jasper has protecting and anchoring qualities. This type of red crystals improves physical vigor, strength, and endurance and connects to the root chakra.
Uses
Red jasper is frequently used to make jewelry, sculptures, and ornamental items. Throughout history, it has served a variety of functional and decorative functions.
Lapidary Art
People use Red jasper to carve, bead, or fashion into cabochons because of its rich color and hardness. It is a well-liked option for fashioning eye-catching jewelry.
Garnet
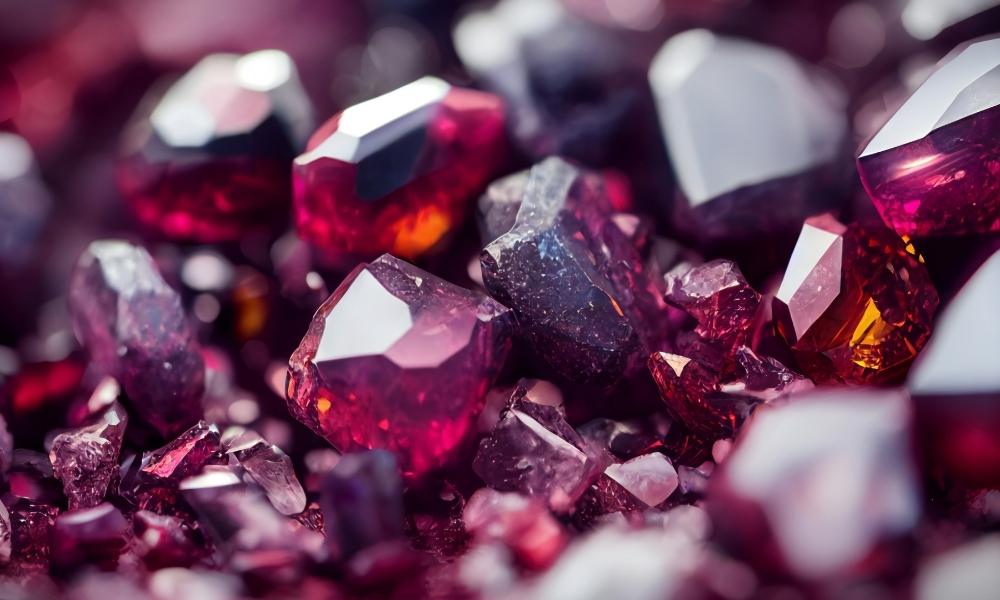

Garnet is also a class of red crystals. Although garnet is a collection of silicate minerals with many different hues, its deep red color is the most well-known. Here are some salient characteristics and details regarding garnet:
Composition
A variety of minerals with varying chemical compositions are part of the garnet group. All of them are silicate minerals, nevertheless, with different amounts of iron, calcium, aluminum, and other elements.
Colors
Garnets are in colors of orange, yellow, green, blue, purple, brown, black, and even colorless, however red is their most common color. In the group, each color belongs to a certain variety of garnets.
Hardness
With a Mohs hardness of 6.5 to 7.5, garnets are robust and appropriate for a variety of jewelry designs.
Types of Garnet
Some common types of garnet include:
Almandine
Typically deep red to brownish-red.
Pyrope
Distinguished by a rich crimson-to-purple-red hue.
Spessartine
Orange to reddish-brown is common.
Grossular
Comes in a variety of hues, including brown, yellow, and green.
Andradite
Comes in a variety of hues, such as yellow and green.
Uvarovite
Typically green in color.
Occurrence
There are garnets in a lot of places throughout the world. India, Sri Lanka, Brazil, Madagascar, Mozambique, and the United States are a few prominent sources.
Symbolism and Uses
Since ancient times, garnet is symbolic of many things, such as strength, regeneration, and protection. It is used to make talismans, amulets, and jewelry. January’s birthstone is garnet as well.
Cut and Jewelry
These red crystals (Garnets) come in a variety of forms, such as cushions, ovals, and rounds. All kinds of jewelry, such as bracelets, necklaces, earrings, and rings, employ them.
Historical Significance
For thousands of years, garnets have been utilized in jewelry and decorative arts. They were especially well-liked in ancient Egypt, where they were frequently utilized as jewelry for burial and as amulets.
Red Tourmaline (Rubellite)
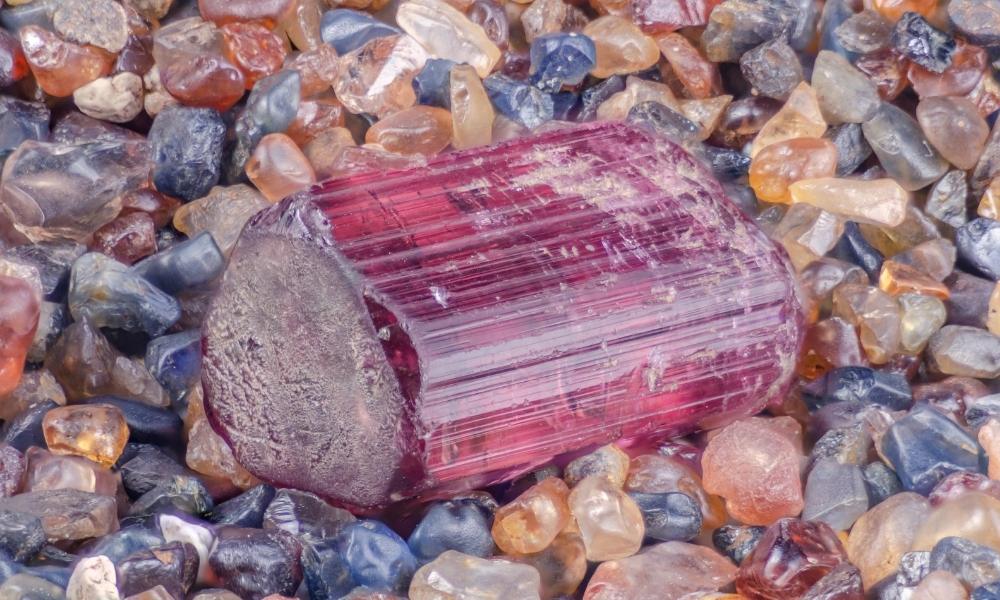

“Rubellite” is the term used to describe red tourmaline when it has a deep red or pinkish-red hue. The red type of tourmaline, a complex boron aluminum silicate mineral with a wide spectrum of hues, is one of the most valuable. Here are some salient characteristics and details regarding rubellite which is a class of red crystals, often known as red tourmaline:
Color
Rubellite’s characteristic red color varies from a rich, intense red to a pinkish-red tint. While there are differences in color intensity, the most prized specimens often have a pure, intense red color.
Composition
The usual formula for these red crystals called tourmaline is (Na, Ca)(Li, Al)3Al6(BO3)3Si6O18(OH)4. Tourmaline is a complicated mineral. Manganese and occasionally lithium ions are responsible for the distinctive hue of rubellites.
Hardness
Rubellite is a kind of tourmaline that ranges in hardness from 7 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale. Because of this, it goes well with many kinds of jewelry.
Occurrence
Rubellite is all over the world, particularly in the US, Brazil, Madagascar, Mozambique, and Afghanistan.
Inclusions
Rubellite may have inclusions, just like many other gemstones. Certain inclusions, including liquid-filled tubes or rutile crystals shaped like needles, can produce unusual optical illusions called “silk.”
Treatment
Rubellite is frequently heated to bring out its color. Buyers must be informed of any treatments a gemstone may have received.
Jewelry
People often wear Jewelry of these red crystals (rubellite), such as bracelets, necklaces, earrings, and rings. It is a desirable option for anyone searching for a stunning gemstone because of its vivid red color.
Symbolism
In general, tourmalines link to several metaphysical characteristics. Some people think that rubellites encourage passion, love, and emotional healing.
Cinnabar
Cinnabar, a striking red to reddish-brown mineral, is the primary mercury ore. It also belongs to a class of red crystals. Here are some salient characteristics and details about cinnabar:
Chemical Composition
With the chemical formula HgS, cinnabar is made up of sulfur (S) and mercury (Hg). This mineral is a sulfide.
Color
The color of red crystals of the Cinnabar type has an intensely unique color, which ranges from bright red to scarlet. The deep scarlet color is due to substances containing mercury.
Occurrence
Cinnabar is around hot spring deposits and in regions where there has been volcanic activity. It often occurs in association with other ore minerals and can form in hydrothermal veins.
Mining and Production
Cinnabar was a significant mercury supplier in the past. Through a procedure known as roasting, mercury is extracted from cinnabar by heating the mineral to cause the mercury vapor to escape and then condense.
Crystal Structure
Cinnabar forms prismatic crystals when it crystallizes in the trigonal system. It is more frequently discovered, although, in large or granular aggregates.
Uses
Cinnabar has historically been used to make vermilion, a crimson pigment that is frequently used in decorations and artwork, because of its mercury concentration. However, because mercury is so hazardous, vermilion is no longer in use.
Toxicity
Because of the mercury in it, cinnabar is toxic. It is usually safe in its natural state, but when crushed or heated, it releases harmful mercury fumes.
Symbolism
In many countries, cinnabar has symbolic and cultural value. The cinnabar powder was employed as a paint for calligraphy and artwork in ancient China, but its toxicity prompted the creation of other pigments.
Red Calcite
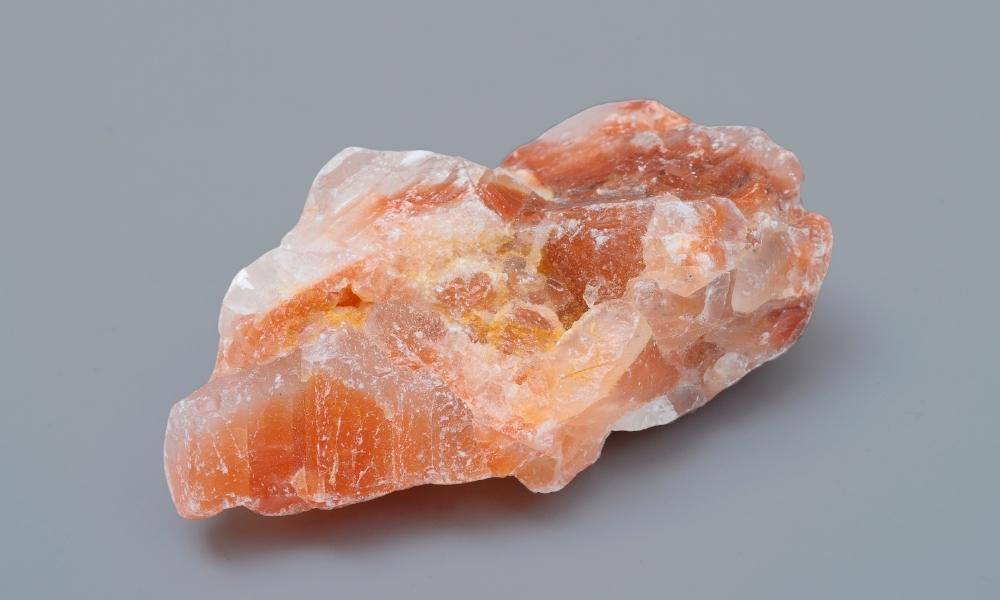

One of the most prevalent carbonate minerals on Earth is calcite, which comes in the variant red calcite. There are several hues of calcite, and inclusions or impurities are usually what give Red Calcite its red hue and is a type of red crystals. The following are some salient characteristics and details of red calcite:
Color
Red calcite, as its name implies, comes in a variety of red hues, from light pink to deep crimson. The presence of contaminants like iron oxide might affect the color.
Chemical Composition
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) makes up this type of red crystals called calcite. Traces of other elements or minerals are frequently the cause of the red coloring.
Transparency
Transparent to translucent red calcite is possible. Its transparency may have an impact on how light interacts with the crystal, enhancing its aesthetic attractiveness.
Crystal Structure
Calcite frequently forms Rhombohedral crystals, which are a member of the trigonal crystal system. Red calcite, however, is typically in granular or large forms.
Hardness
Compared to many other minerals, calcite is rather soft, with a Mohs hardness of 3. Its softness impacts its use in some applications.
Occurrence
Calcite is a mineral that is all over the world. Particularly red calcite is in deposits where various minerals and calcium-rich fluids combine.
Metaphysical Properties
Red Calcite is connected to energy, vigor, and motivation in metaphysical and healing traditions. It improves well-being and assists reduce emotional stress.
Uses
Red calcite is in use as a lapidary material and for decorative reasons, such as in beads and carved sculptures. It can also be added to one’s collection or utilized in crystal healing procedures.
Rhodochrosite
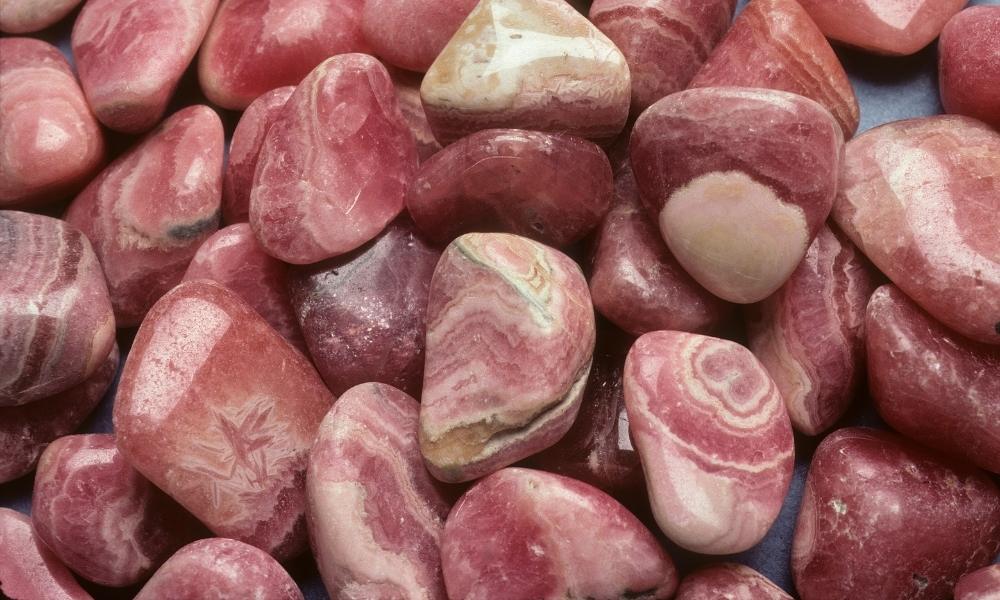

The stunning and unique mineral of red crystals known as rhodochrosite has a rose-pink to reddish-brown hue. The following are salient characteristics and details of rhodochrosite:
Chemical Composition
The chemical formula for the manganese carbonate mineral rhodochrosite is MnCO3. Its distinctive pink hue is due to the manganese content.
Color
Rhodochrosite can be light pink to deep red in hue, with white or gray bands or streaks frequently present. The color’s pattern and intensity might change.
Crystal System
Rhodochrosite usually crystallizes as rhombohedral crystals in the trigonal crystal system. Additionally, it might appear in large or granular forms.
Transparency
One can find transparent or translucent rhodochrosite. Its openness impacts its value and aesthetic appeal.
Hardness
Rhodochrosite is a comparatively soft mineral when compared to many other minerals, with a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4.
Occurrence
Rhodochrosite which is a class of red crystals is all over the world. Argentina, Peru, South Africa, Mexico, and the United States have notable deposits.
Banding
Rhodochrosite frequently has characteristic banding, consisting of layers that are varying colors of pink, white, or gray. The banding enhances the stone’s visual appeal.
Uses
As a highly prized gemstone, rhodochrosite is in use for making jewelry, such as bracelets, necklaces, rings, and earrings. Its distinctive hue and crystal forms also draw collectors of minerals to it.
Metaphysical Properties
Rhodochrosite connects to love, compassion, and emotional healing in metaphysical beliefs. It assists in opening and balancing the heart chakra.
Care
Due to its heat sensitivity, rhodochrosite can fade under direct sunshine. Shield it from acidic materials because it is likewise vulnerable to acids.
Red Agate
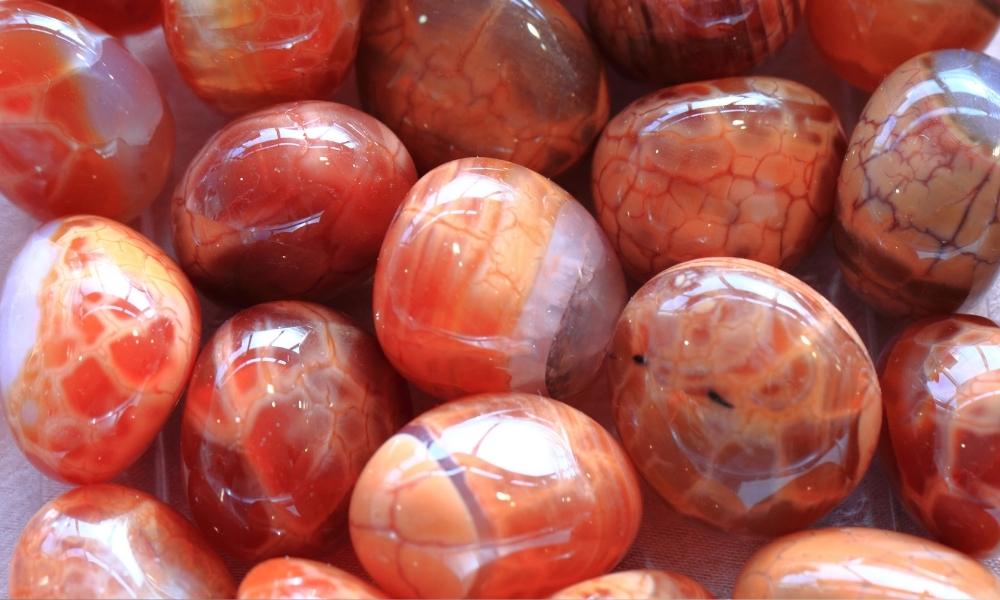

Red crystals have another type known as Red Agate. Red agate is a variation of chalcedony, a kind of microcrystalline quartz. Agate has layers or bands, and red agate in particular has reddish-hued bands or patterns. The following are salient characteristics and details regarding red agate:
Color
Red agate has a range of red colors, from rich crimson to softer pink tones. White or other colored bands or layers are frequently scattered across the red coloring.
Composition
The main component of agate is silicon dioxide (SiO2), which is also the mineral that constitutes quartz. Agate’s characteristic banding is due to a variety of inclusions or impurities.
Transparency
Light can travel through red agate because it can be either transparent or translucent. Its transparency impacts its visual appeal, which is frequently improved by polishing.
Hardness
Agate is a somewhat durable material that is used to make a variety of jewelry and decorative products, with a Mohs hardness of 6.5 to 7.
Occurrence
Around the world, agate is in a variety of places. One can obtain red agate from the United States, Botswana, India, Brazil, and Mexico.
Banding
The banded look of agate is its most distinctive feature. These bands are frequently created throughout the formation process by fluctuations in the concentration of contaminants or alternating layers of distinct minerals.
Cut and Use
Red agate is frequently carved into different shapes or cut into cabochons for use in jewelry such as bracelets, necklaces, earrings, and rings. Additionally, it makes sculptures and ornamental things.
Metaphysical Properties
Red agate is connected to attributes like strength, protection, and anchoring in metaphysical and spiritual ideas. It improves stability and brings the energies into harmony.
Care
Red agate is generally resilient, much like other agate variations, but it should be shielded from corrosive substances, extremely high or low temperatures, and continuous sunlight exposure.
(FAQs) about Red Crystals
Q1. What are red crystals called?
The Best Red Crystals & Gemstones are garnet, carnival, ruby, and Red Jasper.
Q2. What is the red crystal for?
Red crystals are a potent symbol of vitality and life in the body. They will inspire you to live intentionally and assist you in concentrating on the things that matter most in life. Red crystals are symbolic of life, energy, and passion. They will motivate you and help you stay on task.
Q3. Is red crystal good?
Red crystal boosts and fortifies self-assurance. They promote genuine emotions of self-love and acceptance and aid in emotional healing. These red jewels aid in the development of the soul as well. They maximize inner strength and self-empowerment and assist in balancing and aligning the chakras.
Q4. What is the bright red healing crystal?
The Red Carnelian stone is a blazing kiss of life and warmth, a stone of exuberant love and vitality. This healer of the root and sacral chakras removes any obstacles to allow your enthusiasm to flow. In addition to being a strength and self-power stone, carnelian is also referred to as the artist’s stone.
Q5. Is red crystal rare?
Red gemstones have been used by humans as jewelry for generations. True red colors are uncommon in the world of gems, despite the fact that red has long been strongly associated with passion, love, fire, and blood.
Stay Tuned to Gems Tycoon for all gems-related articles.